LVRTM Example Use Case
1 Description of the Use Case
1.1 Name of the Use Case
| ID | Area / Domain(s)/ Zone(s) | Name of the Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 132 | Low Voltage Network Real Time Monitoring (LVRTM) |
1.2 Version Management
1.3 Scope and Objectives of Use Case
| Scope | The use case consists in collecting in a unique repository located in the Secondary Substation – measurement (mean values and PQ indexes), states and alarms from the LV grid. |
|---|---|
| Objective(s) | This information is needed to perform correctly algorithms (State Estimation, State Forecasting, Optimal Power Flow, and control actions in order to increase the network reliability and performance. |
| Related business case(s) |
1.4 Narrative of Use Case
Short description
The data collection for the LV grid is performed storing real-time measurements (mean values and PQ indexes), states and alarms in a unique repository – located in the Secondary Substation – after managing some implementation issues, such as protocol conversion and writing of data into the SSAU.RDBMS.
“Real-time” in this context means something in between 1 second and some minutes.
Complete description
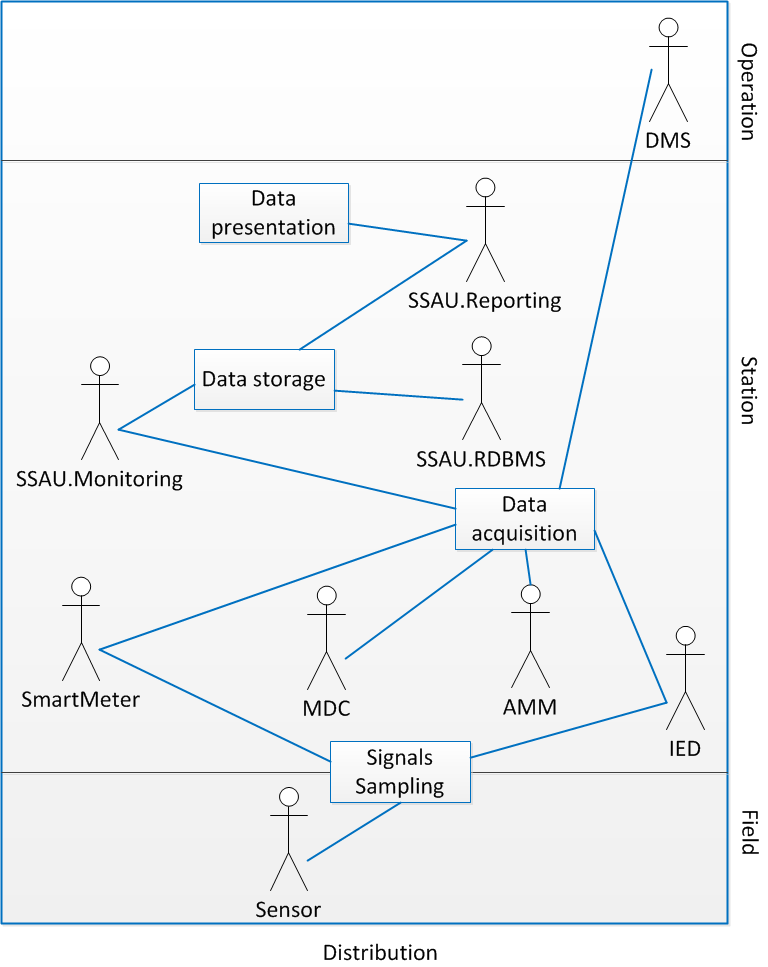
On the LV grid, several monitoring devices will be installed:
- Smart Meters (SM) on the connection point of LV customers/productions. Data of SMs are often collected by a Meter Data Collector (MDC) system, installed in the secondary substation and aggregated in an Automatic Metering Management system (AMM) located in the control center.
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), Power Quality Meters (PQMs) or – more in general – Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs)
Data considered by the use case is:
Mean values of V, I, Q, P:
LV busbars, LV side of transformers and LV lines in secondary substations (RTU, IED)
On the connection point of LV customers/productions (SM/MDC)
Load profiles from LV customers and generations (SM/MDC)
PQ indexes both from the secondary substations and from some relevant nodes of the LV grid, such has street cabinets (PQM)
Status of remote-controllable elements in secondary substations (RTU-IED)
breakers/disconnectors
tap changer of MV/LV transformers
voltage or reactive power set-points for generation connected on the LV network
Alarms related to events and faults (IED-PQM-RTU)
Measures, events and states not provided by those devices are provided by the Distribution Management System (DMS).
Measures, events and states from the MV side of the secondary substation should be considered as well. In that case they will be transfer to the primary substation by the DMS.
Measures are fetched by using:
the IEC61850 protocols (mainly MMS) and stored into the database which presents a data model compliant with the IEC61850 for the general monitoring of the LV grid (from RTUs, IEDs, DMS…)
DLMS/COSEM protocol for the communication with electronic meters(EM)
Protocol conversion have to be implemented before writing the data – collected from different sources – into the SSAU.RDBMS to enable the execution of other use cases.
The SSAU.RDBMS should contain a Data layer, composed by a relational database, where the data are written.
The SSAU.Monitoring must include an Interface layer which implements required communication protocols and which is able to extract data from other systems.
The SSAU.Reporting is composed of an Application layer, which analyses the data to:
calculate statistical values such as min, max, avg, std, etc.
generate reports for the primary substation/DMS
1.5 General Remarks
2 Diagrams of Use Case

3 Technical Details
3.1 Actors
| Actor Name | Actor Type | Actor Description | Further information specific to this Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIED.SM | function | Smart Meter (SM) Def. 1 Meter with additional functionalities one of which is data communication. Def. 2 The metering end device is a combination of the following meter-related functions from the Smart Metering reference architecture: Metrology functions including the conventional meter display (register or index) that are under legal metrological control. When under metrological control, these functions shall meet the essential requirements of the MID; One or more additional functions not covered by the MID. These may also make use of the display; Meter communication functions Actor in the Field zone | |
| DMS.DXP.MMS | function | DXP communication interface Depending on the particolar interface it can be - 104 master - 61850 client/server - Modbus/TCP master Distribution Management System (DMS) Def. 1 Application server of a Distribution Management System which hosts applications to monitor and control a distribution grid from a centralized location, typically the control center. Def. 2 DMS SCADA System refers to the real-time information system and all the elements needed to support all the relevant operational activities and functions used in distribution automation at dispatch centers and control rooms. Actor in Enterprise zone | |
| PSAU.DXP.MMS | function | DXP, client server interface for MMS Primary Substation Automation Unit Monitoring It represents the monitoring functionalities which are implemented in the Primary Substation Automation Unit | |
| Sensor | other | It is a generic sensor such as voltage sensor, current sensor, state sensor, etc. which can be acquired by a generic IED (RTU, PD, etc.) | |
| SSAU.DXP.AMM | function | Automatic Meter Management is the system which is in charged to manage meter data concentrators collecting data in a centralzed database and performing a set of diagnostic functions | |
| SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | SSAU data exchange platform for DLMS/COSEM protocol (smart meter data) | ||
| SSAU.DXP.IEC104 | function | Secondary Substation Automation Unit Reporting It represents the reporting functionalities which are implemented in the Secondary Substation Automation Unit | |
| SSAU.DXP.MMS | function | DXP, client server interface for MMS Secondary Substation Automation Unit Monitoring It represents the monitoring functionalities which are implemented in the Secondary Substation Automation Unit | |
| SSAU.DXP.Modbus | |||
| SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | function | Secondary Substation Automation Unit Relational Database Management System It represents the database and the related management system which compose the Secondary Substation Automation Unit storage system | |
| SSAU.SC | SSAU.SC SSAU statistical calculation | ||
| SSIED | function | PSIED | |
| SSIED.MDC | function | Meter Data Concentrator (MDC) Def. 1 A party responsible for meter reading and quality control of the reading. Def. 2 Device or application typically in a substation which establishes the communication to smart meters to collect the metered information and send it in concentrated form to an AMI head end. Actor in Station zone |
3.2 Triggering Event, Preconditions, Assumptions
| Actor/System/Information/Contract | Triggering Event | Pre-conditions | Assumption |
|---|---|---|---|
3.3 References
| No. | References Type | Reference | Status | Impact on Use Case | Organistaor / Organisation | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3.4 Further Information to the Use Case for Classification / Mapping
Relation to Other Use Cases
Medium Voltage Network Real Time Monitoring (MVRTM);
Level of Depth
Primary Use Case
Priorisation
??
Generic, Regional or National Relation
European
Viewpoint
Technical
Further Keyword for Classification
Low Voltage Grid, Monitoring, Report, DLMS/COSEM
4 Step by Step Analysis of Use Case
4.1 Overview of Scenarios
| No. | Scenario Name | Primary Actor | Triggering Event | Pre-Condition | Post-Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SM with MDC [normal] | Sensor, SM, MDC, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | Each SM is sampling values from connected sensors, MDC is connected to the SMs, SAU.Monitoring can call MDC webservices and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | Smart Meters Data (voltages, currents, powers, etc.) is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
| 2 | SM without MDC [normal] | Sensor, SM, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | Each SM is sampling values from connected sensors, SSAU.Monitoring is connected to the SMs and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | Smart Meters Data (voltages, currents, powers, etc.) is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
| 3 | SM with AMM [normal] | Sensor, SM, AMM, MDC, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | Each SM is sampling values from connected sensors, MDC is connected to the SMs, AMM is connected to the SMs and MDCs, SAU.Monitoring is connected to the AMM and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | Smart Meters Data (voltages, currents, powers, etc.) is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
| 4 | DMS No Monitored Event [normal] | DMS, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | No directly monitored events in the LV grid | DMS recives a notification for an event occured in the LV grid which is not directly monitored by SSAU.Monitoring (i.e. state changed for a manual disconnetor), SSAU.Monitoring has subscribed the related report and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | No monitored event data is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
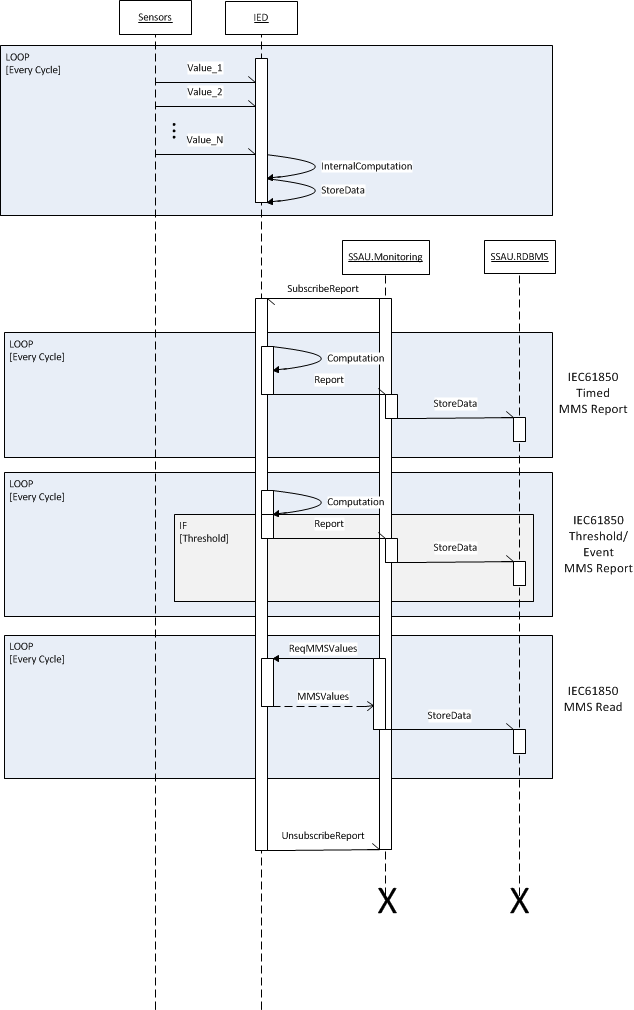
| 5 | IED Timed MMS Report [normal] | Sensor, SSIED, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | IED is sampling values from connected sensors, SSAU.Monitoring has subscribed the IED timed report and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | IED report data is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
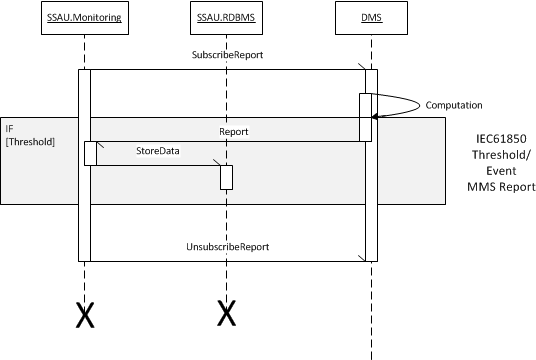
| 6 | IED Threshold/Event MMS Report [normal] | Sensor, SSIED, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Threshold crossed | IED is sampling values from connected sensors, SSAU.Monitoring has subscribed the IED threshold report and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | IED report data is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
| 7 | IED Read MMS [normal] | Sensor, SSIED, SSAU.Monitoring, SSAU.RDBMS | Read request from SSAU.Monitoring | IED is sampling values from connected sensors, SSAU.Monitoring is connected to the IED and SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | IED requested data is stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
| 8 | Reporting Timed Report [normal] | SSAU.Reporting, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | An external entity has subscribed a SSAU.Reporting timed report. SSAU.Reporting and SSAU.RDBMS are available to provide data | Report is transmitted to the external entity |
| 9 | Reporting Threshold Report [normal] | SSAU.Reporting, SSAU.RDBMS | Threshold crossed | An external entity has subscribed a SSAU threshold report. SSAU.Reporting and SSAU.RDBMS are available to provide data | Report is transmitted to the external entity |
| 10 | Reporting Read MMS [normal] | SSAU.Reporting, SSAU.RDBMS | Read request from external entity | An external entity has requested a read data then SSAU.Reporting answers retieving data from SSAU.RDBMS | SSAU requested data is transmitted to the external entity |
| 11 | Statistical Calculation [normal] | SSAU.Reporting, SSAU.RDBMS | Periodically | SSAU.RDBMS is available to store new data | Statistical Values are stored in the SSAU.RDBMS |
4.2 Steps – Scenarios
Scenario Name: No. 1 - SM with MDC [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | SM samples sensors signals (voltages and currents) and calculate powers and energies | REPORT | Sensor | DIED.SM | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude | |
| 2 | Periodically | Data acquisition | MDC acquires data from conneted SMs | GET | DIED.SM | SSIED.MDC | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | Periodically | Data acquisition | SSAU.Monitoring acquires data from MDC | GET | SSIED.MDC | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 4 | SSAU.Moitoring Data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring writes acquired data in SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 2 - SM without MDC [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | SM samples sensors signals (voltages and currents) and calculate powers and energies | REPORT | Sensor | DIED.SM | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude | |
| 2 | Periodically | Data acquisition | SSAU.Monitoring acquires values from connected SMs | GET | DIED.SM | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring writes acquired data in SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 3 - SM with AMM [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | SM samples sensors signals (voltages and currents) and calculate powers and energies | REPORT | Sensor | DIED.SM | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude | |
| 2 | Periodically | Data acquisition | MDC acquires data from conneted SMs | GET | DIED.SM | SSIED.MDC | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | Periodically | Data acquisition | AMM acquires data from conneted MDCs | GET | SSIED.MDC | SSAU.DXP.AMM | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 4 | Periodically | Data acquisition | AMM acquires data from conneted SMs | GET | DIED.SM | SSAU.DXP.AMM | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 5 | Periodically | Data acquisition | SSAU.Monitoring acquires data from conneted AMM | GET | SSAU.DXP.AMM | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 6 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring writes acquired data in SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.DLMS/COSEM | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 4 - DMS No Monitored Event [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Monitored Event from LV grid | Data acquisition | DMS sends a report to the SSAU.Monitoring containing data related to the event | REPORT | DMS.DXP.MMS | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Switch status | |
| 2 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring stores the data received by the DMS into the SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 5 - IED Timed MMS Report [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | IED samples and acquires voltages/currents/states/etc. signals from sensors | REPORT | Sensor | SSIED | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Switch status | |
| 2 | Periodically | Data acquisition | IED generates a new report that will be transmitted to the SSAU.Monitoring. Report can contains one or more values | REPORT | SSIED | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring stores the received report data inside the SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 6 - IED Threshold/Event MMS Report [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | IED samples and acquires voltages/currents/states/etc. signals from sensors | REPORT | Sensor | SSIED | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Switch status | |
| 2 | Threshold crossed | Data acquisition | IED generate a new report that will be transmitted to the SSAU.Monitoring. Report can contains one or more values | REPORT | SSIED | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring stores the received report data inside the SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 7 - IED Read MMS [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Signals sampling | IED samples and acquires voltages/currents/states/etc. signals from sensors | REPORT | Sensor | SSIED | Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Switch status | |
| 2 | Read request | Data acquisition | SSAU.Monitoring requestes a read then IED answers sending the requested values | GET | SSIED | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | SSAU.Monitoring data acquired | Data storage | SSAU.Monitoring stores the received report data inside the SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 8 - Reporting Timed Report [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Data storage | SSAU.Reporting reads data from SSAU.RDBMS | GET | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Statistical measurement Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 2 | SSAU.Reporting data retrieved | Data presentation | SSAU.Reporting generates a new report which contains the data retrieved from SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | PSAU.DXP.MMS | Statistical measurement Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 9 - Reporting Threshold Report [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Data storage | SSAU.Reporting reads data from SSAU.RDBMS | GET | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | SSAU.DXP.MMS | Statistical measurement Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 2 | Threshold crossed | Data presentation | SSAU.Reporting generates a new report if a predefined threshold is crossed | REPORT | SSAU.DXP.MMS | PSAU.DXP.MMS | Statistical measurement Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 10 - Reporting Read MMS [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Read request from external entity | Data presentation | SSAU.Reporting receives a read data request from an external entity so it retrieves data from SSAU.RDBMS | GET | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | SSAU.DXP.MMS SSAU.DXP.Modbus SSAU.DXP.IEC104 | Statistical measurement Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status |
Scenario Name: No. 11 - Statistical Calculation [normal]
| Step No. | Event. | Name of Process/ Activity | Description of Process/ Activity. | Service | Information Producer (Actor) | Information Receiver (Actor) | Information Exchanged | Requirements, R-ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Periodically | Data storage | SSAU.Reporting retrieves data required to calculate new statical values (such as min, max, avg, etc.) | GET | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | SSAU.SC | Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 2 | Data retrieved | Statistical calculation | SSAU.Reporting calculates a set of statistical values | EXECUTE | SSAU.SC | SSAU.SC | Reactive power Current phase angle Voltage phase angle Voltage magnitude Current magnitude Active power Energy measurement Switch status | |
| 3 | Statistical data calculated | Data storage | SSAU.Reporting stores the calculated statical data inside the SSAU.RDBMS | REPORT | SSAU.SC | SSAU.DXP.RDBMS | Statistical measurement |
5 Information Exchanged
| Name of Information (ID) | Description of Information Exchanged | Requirements to information data |
|---|---|---|
| Active power | Active power injection [W] | |
| Current magnitude | Current magnitude [A] | |
| Current phase angle | Current phase angle [rad] | |
| Energy measurement | Energy measurement [Wh] | |
| Reactive power | Reactive power injection [VAr] | |
| Statistical measurement | Statistical values such as min, max, avg, std, etc. | |
| Switch status | Information about devices states (i.e. breaker: open, close, undefined; tap changer position; etc.) | |
| Voltage magnitude | Voltage magnitude [V] | |
| Voltage phase angle | Voltage phase angle [rad] |
6 Requirements (optional)
7 Common Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
8 Custom Information (optional)
| Key | Value | Refers to Section |
|---|---|---|